- Net Framework 4.6.2 Download
- .net Framework 4.6.2 For Mac
- Dot Net Download Page
- Dotnet Hosting Download
Introduction to Mono on macOS
Mono supports macOS version 10.9 (Mavericks) and later.

You can use Mono on macOS to build server, console and GUI applications. Read below for the options available for GUI application development.
If you are interested in creating native GUI applications, use the MonoMac bindings and our MonoDevelop add-in. Read the description on MonoMac for more information on how to get started.
We intend to release.NET 5 in November 2020, with the first preview available in the first half of 2020. It will be supported with future updates to Visual Studio 2019, Visual Studio for Mac and Visual Studio Code. Check out.NET Core is the Future of.NET to understand how.NET 5 relates to.NET Framework.NET 5 =.NET Core vNext. Alternatives to.NET Framework for Windows, Linux, Mac, Web, BSD and more. Filter by license to discover only free or Open Source alternatives. This list contains a total of 10 apps similar to.NET Framework. List updated: 8/28/2020 3:09:00 PM.
Installing Mono on macOS
You can use Mono either as a runtime to run existing application, or as an SDK to develop new applications with Mono.
Visit the download page to find the latest macOS package. Run it and follow the instructions there, you can either get a basic runtime, or a complete runtime plus a software development kit.
If you plan on developing applications with Mono, we suggest that you also install the MonoDevelop IDE after you install Mono.
The Mono package includes:
- The Mono Runtime
- GUI Toolkits: Windows.Forms and Gtk# for macOS.
- Note: the MonoMac GUI toolkit for native macOS GUI development is currently a separate download.
- SDK: C#, Visual Basic compilers, assemblers and tools
- XSP ASP.NET server
- Manual pages.
This package installs as a framework into /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework (the same way the Java packages are installed). The executable binaries can be found in /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/Versions/Current/bin. If you'd like to access the mono manpages you'll have to add /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/Versions/Current/man to your manpath. The macOS Mono package does not include Gtk#, XSP or mod_mono. These will have to be compiled from source.
Our packages currently require macOS 10.9 or better, for older versions, you will need to build from source code.
Using Mono on macOS
At this point, you must use Mono from the command line, the usual set of commands that are available on other ports of Mono are available.
To build applications you can use 'mcs', to run then you can use mono.
From a Terminal shell, you can try it out:
Most users would be using the MonoDevelop IDE to create their projects.
You will have a choice of GUI toolkits for building your application, from pure cross platform, to Mac-specific using MonoMac.
32 and 64 bit support
The Mono packages published on this web site provide both a 32-bit and a 64-bit Mono VM.
Starting from Mono 5.2 the mono command defaults to 64-bit, you can use the --arch=32/64 switch to control the bitness.
The 64 bit support has a few limitations today:
- Our Windows.Forms implementation uses Carbon, and as such, it would not work with a 64-bit Mono.
Building Client Applications
There are a few choices to build client applications on macOS, you should pick the technology that better fits your goals, your choices are:
| Toolkit | Runs on Linux | Runs on Windows | Runs on Mac | Binding Style | License | Status |
| MonoMac | no | no | yes | Strongly typed C# binding to Cocoa APIs | MIT X11 | Actively developed, builds on the design lessons from MonoTouch but still incomplete. This will be the new default binding for Mono on macOS. Separate download. |
| Gtk# | yes | yes | yes | Strongly typed C# binding to the cross platform Gtk+ API. Applications look foreign on macOS. | LGPL v2 | Actively developed, cross platform. Bundled with Mono. |
| Windows.Forms | yes | yes | yes | Cross platform implementation of Microsoft's Windows.Forms. Applications look foreign on macOS. | MIT X11 | The Windows.Forms API was frozen in time by Microsoft. Bundled with Mono. |
| MonObjc | no | no | yes | Binding to the native Cocoa APIs, but requires manual use of Objective-C selectors to work with, relatively thin wrapper around the underlying APIs. | LGPL v3 | Actively developed. Separate download. |
| CocoaSharp | no | no | yes | Binding to the native Cocoa APIs, but requires manual use of Objective-C selectors to work with, relatively thin wrapper around the underlying APIs. | MIT X11 | No longer developed, no longer maintained, deprecated. Bundled with Mono. |

Running Mono applications on macOS
Running applications on macOS is very similar to linux systems, from the terminal:
For GTK# applications, it's easiest to run them the same way but using xterm from X11.app
Windows.Forms
Mono's implementation of the System.Windows.Forms API is built on top of Carbon and can only run with Mono on 32 bit systems. The look and feel of System.Windows.Forms applications mimics the Windows style and does not currently render like a native macOS application.
Third Party Libraries
ObjC# is a transparent two way bridge that allows the CLR to access the rich underlying ObjectiveC frameworks as well as providing direct access to the CLR frameworks from the ObjectiveC language.
Uninstalling Mono on macOS
Run this script in a terminal:
The OS X frameworks provide the interfaces you need to write software for Mac. Some of these frameworks contain simple sets of interfaces while others contain multiple subframeworks. Where applicable, the tables in this appendix list the key prefixes used by the classes, methods, functions, types, or constants of the framework. You should avoid using any of the specified prefixes in your own symbol names.
System Frameworks
Table A-1 describes the frameworks located in the /System/Library/Frameworks directory and lists the first version of OS X in which each became available.
Name | First available | Prefixes | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.3 |
| Umbrella framework for vector-optimized operations. See Accelerate Framework. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides access to user accounts stored in the Accounts database. See Accounts Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Provides access to the Address Book, which is a centralized database of user contact information. Apps that target OS X v10.11 or greater should use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains Carbon interfaces for OpenGL. See AGL Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains classes and methods for the Cocoa user-interface layer. In general, link to | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for creating AppleScript plug-ins. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C extensions for creating AppleScript plug-ins. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for several app-level services. See Application Services Framework. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for getting audio stream data, routing audio signals through audio units, converting between audio formats, and playing back music. See Audio Toolbox Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for defining Core Audio plug-ins. See Audio Unit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Supports Audio Video Bridging (AVB) and implements the IEEE P1722.1 draft standard. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Umbrella framework for creating Automator plug-ins. See Automator Framework. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Provides interfaces for playing, recording, inspecting, and editing audiovisual media. See AVFoundation Audio Functions. | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API for media playback including user controls, chapter navigation, subtitles, and closed captioning. See AV Kit Framework Reference | |||
| 10.5 |
| Deprecated. Use Event Kit instead. See Event Kit. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for Carbon-level services. See Carbon Framework. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for network communication using HTTP, sockets, and Bonjour. See CFNetwork Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Provides a conduit for moving data between your app and iCloud that can be used for all types of data. It also gives you control of when transfers occur. See CloudKit Quick Start or CloudKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Wrapper for including the Cocoa frameworks | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for managing identity information. See Collaboration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.11 |
| Provides access to the Contacts store, which is a centralized database of user contact information. See Contacts Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the hardware abstraction layer interface for manipulating audio. See Core Audio Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains the classes used for communicating with Bluetooth Low Energy devices. See Core Bluetooth Framework Reference | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for audio unit custom views. See CoreAudioKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for managing your app's data model. See Core Data Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Provides fundamental software services, including abstractions for common data types, string utilities, collection utilities, plug-in support, resource management, preferences, and XML parsing. See Core Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the Quartz interfaces for creating graphic content and rendering that content to the screen. See Core Graphics Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| An image processing and analysis technology designed to provide near real-time processing for still and video images. See Core Image Programming Guide. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Provides interfaces for determining the geographical location of a computer. See Core Location Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for for managing and and playing audio-visual media in an app. See Core Media Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces of the Device Abstraction Layer (DAL) used for creating plug-ins that can access media hardware. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains utilities for implementing MIDI client programs. See Core MIDI Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.6. Use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for system-level services. See Core Services Framework. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains the interfaces for performing text layout and display. See Core Text Reference Collection. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for managing video-based content. See Core Video Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for managing wireless networks. See CoreWLAN Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains interface for using smart cards. See CryptoTokenKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.6. Use | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for burning data to CDs and DVDs. See Disc Recording Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains the user interface layer for interacting with users during the burning of CDs and DVDs. See Disc Recording UI Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for getting information related to local and remote volumes. See Disk Arbitration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the game sprocket component for drawing content to the screen. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with digital video devices, such as video cameras. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for embedding DVD playback features into your app. See DVD Playback Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides an interface for accessing a user's calendar events and reminder items. See Event Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains exception-handling classes for Cocoa apps. See Exception Handling Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Provides API for enhancing the Finder's user interface by adding badges, shortcut menu items, and toolbar buttons. See Finder Sync Framework Reference | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with force feedback–enabled devices. See Force Feedback Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the classes and methods for the Cocoa Foundation layer. If you are creating a Cocoa app, linking to the Cocoa framework is preferable. See Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with FireWire-based audio devices. See FWAUserLib.h Reference. | |||
| 10.9 |
| A collection of classes for discovering and interacting with connected game controllers. See Game Controller Programming Guide | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides APIs that allow your app to participate in Game Center. See Game Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides functions and classes that reduce the effort required to create new shader-based apps or to port existing apps that rely on fixed-function vertex or fragment processing provided by earlier versions of OpenGL ES or OpenGL. See GLKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for the OpenGL Utility Toolkit, which provides a platform-independent interface for managing windows. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces for Generic Security Services Application Program Interface (GSSAPI). | |||
| 10.10 |
| Allows virtualization vendors to build virtualization solutions on top of OS X without needing to deploy third-party kernel extensions (KEXTs). See Hypervisor Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for communicating with digital devices such as scanners and cameras. See Carbon Framework. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for communicating with digital devices such as scanners and cameras. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for importing and exporting image data. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces for building third-party plug-ins for Chat services. Umbrella framework for | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for developing new input methods, which are modules that handle text entry for complex languages. See Input Method Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for creating plug-ins that run during software installation sessions. See Installer JavaScript Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Do not use. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with Bluetooth devices. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains the user interface layer for interacting with users manipulating Bluetooth devices. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the main interfaces for creating user-space device drivers and for interacting with kernel-resident drivers from user space. See IOKitLib.h Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for sharing graphics surfaces between apps. See IOSurface Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 | N/A | Contains interfaces for embedding Java frames in Objective-C code. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains the library and resources for executing JavaScript code within an HTML page. (Prior to OS X v10.5, this framework was part of | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use Oracle Java instead. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for using the Kerberos network authentication protocol. | |||
| 10.0 | numerous | Contains the interfaces for kernel-extension development, including Mach, BSD, | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for classifying text based on latent semantic information. See Latent Semantic Mapping Reference. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Do not use. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains API for requesting authentication from users using specified policies. See Local Authentication Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides classes and protocols for embedding maps into the windows and views of your apps. Includes support for annotations, overlays, and reverse-geocoding lookups. See Map Kit Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API to access user preferences for captions that can accompany media, such as closed captioning. See Media Accessibility Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides a read-only data model representing a user's collections of images, audio, and video. See Media Library Framework Reference | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains Cocoa extensions for mail delivery. | |||
| 10.11 | MTL | Provides GPU-accelerated 3D graphics rendering and> Example Path: '/Users/%accountname%/Documents/Boot/'ntp-servers – Is a given NTP server/service used. Example: 'time.euro.apple.com'sshkeys-file – Is the location to where SSH keys can be accessed, in this case we created them in the SSHKeys folder. Parallels for mac osx. idrsa.pubIn Safari enter the URL for downloading the PmmOsdImageBuilder.dmg file:downloaded mount the PmmOsdImageBuilder.dmg file.In the Terminal application navigate to the mounted folder.Example: 'cd /Volumes/Parallels OSD Image Builder 4.0.1.31/'Run the following command. Sudo./pmmosdimagebuilder netboot -n output-dir -ntp-servers ntpservers -ssh-authkeys sshkeysfileoutput-dir - Is a local folder on the Mac device, in this case the local folder we created called Boot.
| 10.11 | MTK | Contains functions and classes that reduce the effort required to create a Metal application. See MetalKit Framework Reference and MetalKit Functions Reference. |
| 10.11 | MDL | Provides classes that support import, export, and editing of 3D model assets and related resources. See ModelIO Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains API for finding and communicating with services provided by nearby devices using infrastructure Wi-Fi networks, peer-to-peer Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth personal area networks. See Multipeer Connectivity Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for working with network file systems. | |||
| 10.11 |
| Provides support for configuring and controlling Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels. See Network Extension Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains the interfaces for creating and managing extensions in the Today view of the Notification Center. See Notification Center Framework Reference | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains the interfaces for OpenAL, a cross-platform 3D audio delivery library. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains the interfaces for distributing general-purpose computational tasks across the available GPUs and CPUs of a computer. See OpenCL Programming Guide for Mac. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for managing Open Directory information. See Open Directory Programming Guide. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the interfaces for OpenGL, which is a cross-platform 2D and 3D graphics rendering library. See OpenGL Programming Guide for Mac. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for managing and executing OSA-compliant scripts from Cocoa apps. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for interacting with smart card devices. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for implementing custom modules for the System Preferences app. See Preference Panes Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for subscribing to RSS and Atom feeds. See Publication Subscription Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use | |||
| 10.4 |
| Umbrella framework for Quartz services. See Quartz Framework. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains the interfaces for Core Image, Core Animation, and Core Video. See Quartz Core Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for generating thumbnail previews of documents. See Quick Look Framework Reference for Mac. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use | |||
| 10.5 | N/A | Contains interfaces for the Ruby scripting language. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides a high-level, Objective-C API to efficiently load, manipulate, and render 3D scenes in an app. See SceneKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Contains interfaces for writing screen savers. See Screen Saver Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for running scripts from Objective-C code. See Scripting Bridge Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for system-level user authentication and authorization. See Security Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains Cocoa interfaces for authorizing users. See Security Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains the user interface layer for authorizing users in Cocoa apps. See Security Interface Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for loading, unloading and managing | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides an API for sending requests to supported social networking services that can perform operations on behalf of users. See Social Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API for animating arbitrary textured images, or sprites. It includes sound playback, a physics engine, and a rendering loop. See SpriteKit Programming Guide | |||
| 10.7 |
| Supports requesting payment from a user to purchase additional functionality or content from the Mac App Store. See Store Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Do not use. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing network configuration and reachability information. See System Configuration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing the system's Tcl interpreter from an app. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing the system's Tk toolbox from an app. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing TWAIN-compliant image-scanning hardware. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.7 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.11. Use | |||
| 10.8 |
| Comprises the 64-bit replacement for the QuickTime Image Compression Manager. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Umbrella framework for rendering HTML content. See WebKit Framework. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.8. Contains interfaces for connecting to and managing computing cluster software. |
OS X contains several umbrella frameworks for major areas of functionality. Umbrella frameworks group several related frameworks into a larger framework that can be included in your project. When writing software, link your project against the umbrella framework; do not try to link directly to any of its subframeworks. The following sections describe the contents of the umbrella frameworks in OS X.
Accelerate Framework
Table A-2 lists the subframeworks of the Accelerate framework (Accelerate.framework). If you are developing apps for earlier versions of OS X, vecLib.framework is available as a standalone framework.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains vector-optimized interfaces for performing math, big-number, and DSP calculations, among others. |
| Contains vector-optimized interfaces for manipulating image data. |
Application Services Framework

Table A-3 lists the subframeworks of the Application Services framework (ApplicationServices.framework) that are not links to top level frameworks. These frameworks provide C-based interfaces and are intended primarily for Carbon apps, although other programs can use them. The listed frameworks are available in all versions of OS X unless otherwise noted.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Deprecated in OS X v10.8. Use |
| Contains interfaces for color matching using ColorSync. |
| Contains interfaces for accessibility, Internet Config, the pasteboard, the Process Manager, and the Translation Manager. Available in OS X v10.2 and later. |
| Contains the Language Analysis Manager interfaces. |
| Contains the Core Printing Manager interfaces. |
| Contains the QuickDraw interfaces. |
| Contains the Speech Manager interfaces. |
Automator Framework
Table A-4 lists the subframeworks of the Automator framework (Automator.framework).
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains private interfaces for managing Automator plug-ins. |
Carbon Framework
Table A-5 lists the subframeworks of the Carbon framework (Carbon.framework). The listed frameworks are available in all versions of OS X unless otherwise noted.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Deprecated in OS X v10.5. Use |
| Contains interfaces for displaying the Font window, Color window, and some network-related dialogs. |
| Contains interfaces for launching and searching Apple Help. |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use |
| Contains interfaces for rendering HTML content. The WebKit framework is the preferred framework for HTML rendering. See WebKit Framework. |
| Contains interfaces for capturing images from digital cameras. This framework works in conjunction with the Image Capture Devices framework ( |
| Contains interfaces for managing pen-based input. (Ink events are defined with the Carbon Event Manager.) |
| Contains interfaces for displaying file navigation dialogs. |
| Contains interfaces for writing scripting components and interacting with those components to manipulate and execute scripts. |
| Contains the Carbon Printing Manager interfaces for displaying printing dialogs and extensions. |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use |
| Contains the Speech Recognition Manager interfaces. |
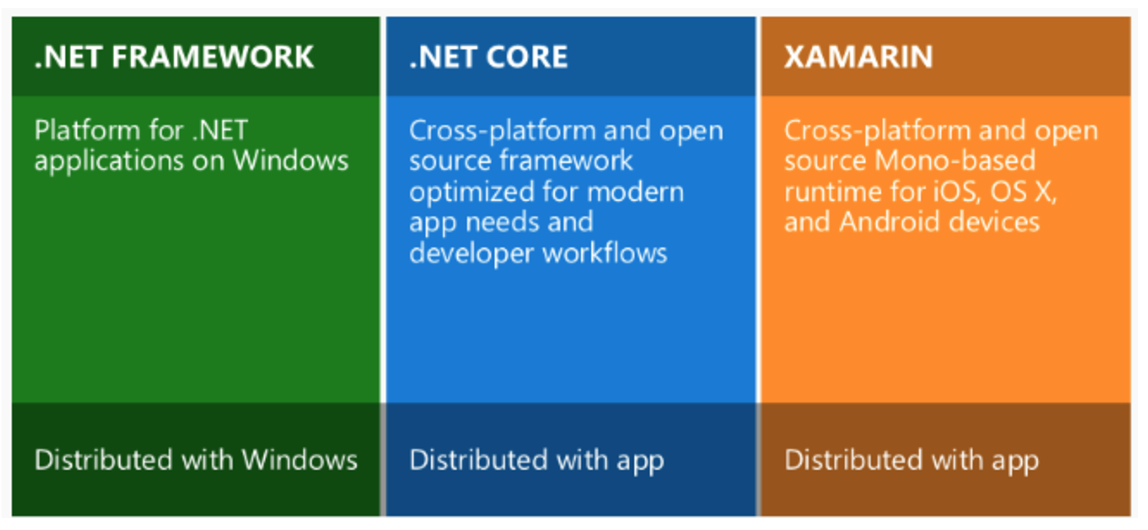
Net Framework 4.6.2 Download
You can use Mono on macOS to build server, console and GUI applications. Read below for the options available for GUI application development.
If you are interested in creating native GUI applications, use the MonoMac bindings and our MonoDevelop add-in. Read the description on MonoMac for more information on how to get started.
We intend to release.NET 5 in November 2020, with the first preview available in the first half of 2020. It will be supported with future updates to Visual Studio 2019, Visual Studio for Mac and Visual Studio Code. Check out.NET Core is the Future of.NET to understand how.NET 5 relates to.NET Framework.NET 5 =.NET Core vNext. Alternatives to.NET Framework for Windows, Linux, Mac, Web, BSD and more. Filter by license to discover only free or Open Source alternatives. This list contains a total of 10 apps similar to.NET Framework. List updated: 8/28/2020 3:09:00 PM.
Installing Mono on macOS
You can use Mono either as a runtime to run existing application, or as an SDK to develop new applications with Mono.
Visit the download page to find the latest macOS package. Run it and follow the instructions there, you can either get a basic runtime, or a complete runtime plus a software development kit.
If you plan on developing applications with Mono, we suggest that you also install the MonoDevelop IDE after you install Mono.
The Mono package includes:
- The Mono Runtime
- GUI Toolkits: Windows.Forms and Gtk# for macOS.
- Note: the MonoMac GUI toolkit for native macOS GUI development is currently a separate download.
- SDK: C#, Visual Basic compilers, assemblers and tools
- XSP ASP.NET server
- Manual pages.
This package installs as a framework into /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework (the same way the Java packages are installed). The executable binaries can be found in /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/Versions/Current/bin. If you'd like to access the mono manpages you'll have to add /Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/Versions/Current/man to your manpath. The macOS Mono package does not include Gtk#, XSP or mod_mono. These will have to be compiled from source.
Our packages currently require macOS 10.9 or better, for older versions, you will need to build from source code.
Using Mono on macOS
At this point, you must use Mono from the command line, the usual set of commands that are available on other ports of Mono are available.
To build applications you can use 'mcs', to run then you can use mono.
From a Terminal shell, you can try it out:
Most users would be using the MonoDevelop IDE to create their projects.
You will have a choice of GUI toolkits for building your application, from pure cross platform, to Mac-specific using MonoMac.
32 and 64 bit support
The Mono packages published on this web site provide both a 32-bit and a 64-bit Mono VM.
Starting from Mono 5.2 the mono command defaults to 64-bit, you can use the --arch=32/64 switch to control the bitness.
The 64 bit support has a few limitations today:
- Our Windows.Forms implementation uses Carbon, and as such, it would not work with a 64-bit Mono.
Building Client Applications
There are a few choices to build client applications on macOS, you should pick the technology that better fits your goals, your choices are:
| Toolkit | Runs on Linux | Runs on Windows | Runs on Mac | Binding Style | License | Status |
| MonoMac | no | no | yes | Strongly typed C# binding to Cocoa APIs | MIT X11 | Actively developed, builds on the design lessons from MonoTouch but still incomplete. This will be the new default binding for Mono on macOS. Separate download. |
| Gtk# | yes | yes | yes | Strongly typed C# binding to the cross platform Gtk+ API. Applications look foreign on macOS. | LGPL v2 | Actively developed, cross platform. Bundled with Mono. |
| Windows.Forms | yes | yes | yes | Cross platform implementation of Microsoft's Windows.Forms. Applications look foreign on macOS. | MIT X11 | The Windows.Forms API was frozen in time by Microsoft. Bundled with Mono. |
| MonObjc | no | no | yes | Binding to the native Cocoa APIs, but requires manual use of Objective-C selectors to work with, relatively thin wrapper around the underlying APIs. | LGPL v3 | Actively developed. Separate download. |
| CocoaSharp | no | no | yes | Binding to the native Cocoa APIs, but requires manual use of Objective-C selectors to work with, relatively thin wrapper around the underlying APIs. | MIT X11 | No longer developed, no longer maintained, deprecated. Bundled with Mono. |
Running Mono applications on macOS
Running applications on macOS is very similar to linux systems, from the terminal:
For GTK# applications, it's easiest to run them the same way but using xterm from X11.app
Windows.Forms
Mono's implementation of the System.Windows.Forms API is built on top of Carbon and can only run with Mono on 32 bit systems. The look and feel of System.Windows.Forms applications mimics the Windows style and does not currently render like a native macOS application.
Third Party Libraries
ObjC# is a transparent two way bridge that allows the CLR to access the rich underlying ObjectiveC frameworks as well as providing direct access to the CLR frameworks from the ObjectiveC language.
Uninstalling Mono on macOS
Run this script in a terminal:
The OS X frameworks provide the interfaces you need to write software for Mac. Some of these frameworks contain simple sets of interfaces while others contain multiple subframeworks. Where applicable, the tables in this appendix list the key prefixes used by the classes, methods, functions, types, or constants of the framework. You should avoid using any of the specified prefixes in your own symbol names.
System Frameworks
Table A-1 describes the frameworks located in the /System/Library/Frameworks directory and lists the first version of OS X in which each became available.
Name | First available | Prefixes | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.3 |
| Umbrella framework for vector-optimized operations. See Accelerate Framework. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides access to user accounts stored in the Accounts database. See Accounts Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Provides access to the Address Book, which is a centralized database of user contact information. Apps that target OS X v10.11 or greater should use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains Carbon interfaces for OpenGL. See AGL Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains classes and methods for the Cocoa user-interface layer. In general, link to | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for creating AppleScript plug-ins. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C extensions for creating AppleScript plug-ins. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for several app-level services. See Application Services Framework. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for getting audio stream data, routing audio signals through audio units, converting between audio formats, and playing back music. See Audio Toolbox Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for defining Core Audio plug-ins. See Audio Unit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Supports Audio Video Bridging (AVB) and implements the IEEE P1722.1 draft standard. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Umbrella framework for creating Automator plug-ins. See Automator Framework. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Provides interfaces for playing, recording, inspecting, and editing audiovisual media. See AVFoundation Audio Functions. | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API for media playback including user controls, chapter navigation, subtitles, and closed captioning. See AV Kit Framework Reference | |||
| 10.5 |
| Deprecated. Use Event Kit instead. See Event Kit. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for Carbon-level services. See Carbon Framework. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for network communication using HTTP, sockets, and Bonjour. See CFNetwork Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Provides a conduit for moving data between your app and iCloud that can be used for all types of data. It also gives you control of when transfers occur. See CloudKit Quick Start or CloudKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Wrapper for including the Cocoa frameworks | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for managing identity information. See Collaboration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.11 |
| Provides access to the Contacts store, which is a centralized database of user contact information. See Contacts Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the hardware abstraction layer interface for manipulating audio. See Core Audio Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains the classes used for communicating with Bluetooth Low Energy devices. See Core Bluetooth Framework Reference | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for audio unit custom views. See CoreAudioKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for managing your app's data model. See Core Data Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Provides fundamental software services, including abstractions for common data types, string utilities, collection utilities, plug-in support, resource management, preferences, and XML parsing. See Core Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the Quartz interfaces for creating graphic content and rendering that content to the screen. See Core Graphics Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| An image processing and analysis technology designed to provide near real-time processing for still and video images. See Core Image Programming Guide. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Provides interfaces for determining the geographical location of a computer. See Core Location Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for for managing and and playing audio-visual media in an app. See Core Media Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces of the Device Abstraction Layer (DAL) used for creating plug-ins that can access media hardware. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains utilities for implementing MIDI client programs. See Core MIDI Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.6. Use | |||
| 10.0 |
| Umbrella framework for system-level services. See Core Services Framework. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains the interfaces for performing text layout and display. See Core Text Reference Collection. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for managing video-based content. See Core Video Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for managing wireless networks. See CoreWLAN Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains interface for using smart cards. See CryptoTokenKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.6. Use | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for burning data to CDs and DVDs. See Disc Recording Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains the user interface layer for interacting with users during the burning of CDs and DVDs. See Disc Recording UI Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for getting information related to local and remote volumes. See Disk Arbitration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the game sprocket component for drawing content to the screen. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with digital video devices, such as video cameras. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for embedding DVD playback features into your app. See DVD Playback Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides an interface for accessing a user's calendar events and reminder items. See Event Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains exception-handling classes for Cocoa apps. See Exception Handling Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Provides API for enhancing the Finder's user interface by adding badges, shortcut menu items, and toolbar buttons. See Finder Sync Framework Reference | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with force feedback–enabled devices. See Force Feedback Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the classes and methods for the Cocoa Foundation layer. If you are creating a Cocoa app, linking to the Cocoa framework is preferable. See Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with FireWire-based audio devices. See FWAUserLib.h Reference. | |||
| 10.9 |
| A collection of classes for discovering and interacting with connected game controllers. See Game Controller Programming Guide | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides APIs that allow your app to participate in Game Center. See Game Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides functions and classes that reduce the effort required to create new shader-based apps or to port existing apps that rely on fixed-function vertex or fragment processing provided by earlier versions of OpenGL ES or OpenGL. See GLKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for the OpenGL Utility Toolkit, which provides a platform-independent interface for managing windows. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces for Generic Security Services Application Program Interface (GSSAPI). | |||
| 10.10 |
| Allows virtualization vendors to build virtualization solutions on top of OS X without needing to deploy third-party kernel extensions (KEXTs). See Hypervisor Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for communicating with digital devices such as scanners and cameras. See Carbon Framework. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for communicating with digital devices such as scanners and cameras. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for importing and exporting image data. | |||
| 10.7 |
| Contains interfaces for building third-party plug-ins for Chat services. Umbrella framework for | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for developing new input methods, which are modules that handle text entry for complex languages. See Input Method Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for creating plug-ins that run during software installation sessions. See Installer JavaScript Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Do not use. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for communicating with Bluetooth devices. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains the user interface layer for interacting with users manipulating Bluetooth devices. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the main interfaces for creating user-space device drivers and for interacting with kernel-resident drivers from user space. See IOKitLib.h Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains low-level interfaces for sharing graphics surfaces between apps. See IOSurface Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 | N/A | Contains interfaces for embedding Java frames in Objective-C code. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains the library and resources for executing JavaScript code within an HTML page. (Prior to OS X v10.5, this framework was part of | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use Oracle Java instead. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for using the Kerberos network authentication protocol. | |||
| 10.0 | numerous | Contains the interfaces for kernel-extension development, including Mach, BSD, | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for classifying text based on latent semantic information. See Latent Semantic Mapping Reference. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Do not use. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains API for requesting authentication from users using specified policies. See Local Authentication Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides classes and protocols for embedding maps into the windows and views of your apps. Includes support for annotations, overlays, and reverse-geocoding lookups. See Map Kit Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API to access user preferences for captions that can accompany media, such as closed captioning. See Media Accessibility Framework Reference | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides a read-only data model representing a user's collections of images, audio, and video. See Media Library Framework Reference | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains Cocoa extensions for mail delivery. | |||
| 10.11 | MTL | Provides GPU-accelerated 3D graphics rendering and> Example Path: '/Users/%accountname%/Documents/Boot/'ntp-servers – Is a given NTP server/service used. Example: 'time.euro.apple.com'sshkeys-file – Is the location to where SSH keys can be accessed, in this case we created them in the SSHKeys folder. Parallels for mac osx. idrsa.pubIn Safari enter the URL for downloading the PmmOsdImageBuilder.dmg file:downloaded mount the PmmOsdImageBuilder.dmg file.In the Terminal application navigate to the mounted folder.Example: 'cd /Volumes/Parallels OSD Image Builder 4.0.1.31/'Run the following command. Sudo./pmmosdimagebuilder netboot -n output-dir -ntp-servers ntpservers -ssh-authkeys sshkeysfileoutput-dir - Is a local folder on the Mac device, in this case the local folder we created called Boot.
| 10.11 | MTK | Contains functions and classes that reduce the effort required to create a Metal application. See MetalKit Framework Reference and MetalKit Functions Reference. |
| 10.11 | MDL | Provides classes that support import, export, and editing of 3D model assets and related resources. See ModelIO Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains API for finding and communicating with services provided by nearby devices using infrastructure Wi-Fi networks, peer-to-peer Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth personal area networks. See Multipeer Connectivity Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for working with network file systems. | |||
| 10.11 |
| Provides support for configuring and controlling Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels. See Network Extension Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.10 |
| Contains the interfaces for creating and managing extensions in the Today view of the Notification Center. See Notification Center Framework Reference | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains the interfaces for OpenAL, a cross-platform 3D audio delivery library. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains the interfaces for distributing general-purpose computational tasks across the available GPUs and CPUs of a computer. See OpenCL Programming Guide for Mac. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for managing Open Directory information. See Open Directory Programming Guide. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains the interfaces for OpenGL, which is a cross-platform 2D and 3D graphics rendering library. See OpenGL Programming Guide for Mac. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for managing and executing OSA-compliant scripts from Cocoa apps. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for interacting with smart card devices. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for implementing custom modules for the System Preferences app. See Preference Panes Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for subscribing to RSS and Atom feeds. See Publication Subscription Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use | |||
| 10.4 |
| Umbrella framework for Quartz services. See Quartz Framework. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains the interfaces for Core Image, Core Animation, and Core Video. See Quartz Core Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for generating thumbnail previews of documents. See Quick Look Framework Reference for Mac. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use | |||
| 10.5 | N/A | Contains interfaces for the Ruby scripting language. | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides a high-level, Objective-C API to efficiently load, manipulate, and render 3D scenes in an app. See SceneKit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Contains interfaces for writing screen savers. See Screen Saver Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.5 |
| Contains interfaces for running scripts from Objective-C code. See Scripting Bridge Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for system-level user authentication and authorization. See Security Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains Cocoa interfaces for authorizing users. See Security Foundation Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains the user interface layer for authorizing users in Cocoa apps. See Security Interface Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.6 |
| Contains interfaces for loading, unloading and managing | |||
| 10.8 |
| Provides an API for sending requests to supported social networking services that can perform operations on behalf of users. See Social Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.9 |
| Provides API for animating arbitrary textured images, or sprites. It includes sound playback, a physics engine, and a rendering loop. See SpriteKit Programming Guide | |||
| 10.7 |
| Supports requesting payment from a user to purchase additional functionality or content from the Mac App Store. See Store Kit Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Do not use. | |||
| 10.0 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing network configuration and reachability information. See System Configuration Framework Reference. | |||
| 10.3 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing the system's Tcl interpreter from an app. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing the system's Tk toolbox from an app. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Contains interfaces for accessing TWAIN-compliant image-scanning hardware. | |||
| 10.0 | N/A | Deprecated. Use | |||
| 10.7 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.11. Use | |||
| 10.8 |
| Comprises the 64-bit replacement for the QuickTime Image Compression Manager. | |||
| 10.2 |
| Umbrella framework for rendering HTML content. See WebKit Framework. | |||
| 10.4 |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.8. Contains interfaces for connecting to and managing computing cluster software. |
OS X contains several umbrella frameworks for major areas of functionality. Umbrella frameworks group several related frameworks into a larger framework that can be included in your project. When writing software, link your project against the umbrella framework; do not try to link directly to any of its subframeworks. The following sections describe the contents of the umbrella frameworks in OS X.
Accelerate Framework
Table A-2 lists the subframeworks of the Accelerate framework (Accelerate.framework). If you are developing apps for earlier versions of OS X, vecLib.framework is available as a standalone framework.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains vector-optimized interfaces for performing math, big-number, and DSP calculations, among others. |
| Contains vector-optimized interfaces for manipulating image data. |
Application Services Framework
Table A-3 lists the subframeworks of the Application Services framework (ApplicationServices.framework) that are not links to top level frameworks. These frameworks provide C-based interfaces and are intended primarily for Carbon apps, although other programs can use them. The listed frameworks are available in all versions of OS X unless otherwise noted.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Deprecated in OS X v10.8. Use |
| Contains interfaces for color matching using ColorSync. |
| Contains interfaces for accessibility, Internet Config, the pasteboard, the Process Manager, and the Translation Manager. Available in OS X v10.2 and later. |
| Contains the Language Analysis Manager interfaces. |
| Contains the Core Printing Manager interfaces. |
| Contains the QuickDraw interfaces. |
| Contains the Speech Manager interfaces. |
Automator Framework
Table A-4 lists the subframeworks of the Automator framework (Automator.framework).
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains private interfaces for managing Automator plug-ins. |
Carbon Framework
Table A-5 lists the subframeworks of the Carbon framework (Carbon.framework). The listed frameworks are available in all versions of OS X unless otherwise noted.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Deprecated in OS X v10.5. Use |
| Contains interfaces for displaying the Font window, Color window, and some network-related dialogs. |
| Contains interfaces for launching and searching Apple Help. |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.7. Use |
| Contains interfaces for rendering HTML content. The WebKit framework is the preferred framework for HTML rendering. See WebKit Framework. |
| Contains interfaces for capturing images from digital cameras. This framework works in conjunction with the Image Capture Devices framework ( |
| Contains interfaces for managing pen-based input. (Ink events are defined with the Carbon Event Manager.) |
| Contains interfaces for displaying file navigation dialogs. |
| Contains interfaces for writing scripting components and interacting with those components to manipulate and execute scripts. |
| Contains the Carbon Printing Manager interfaces for displaying printing dialogs and extensions. |
| Deprecated in OS X v10.9. Use |
| Contains the Speech Recognition Manager interfaces. |
Net Framework 4.6.2 Download
Core Services Framework
Table A-6 lists the subframeworks of the Core Services framework (CoreServices.framework). These frameworks provide C-based interfaces and are intended primarily for Carbon apps, although other programs can use them. The listed frameworks are available in all versions of OS X unless otherwise noted.
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains interfaces for creating and manipulating Apple events and making apps scriptable. |
| Contains interfaces for many legacy Carbon Managers. Most of the APIs in this framework are deprecated in OS X v10.8 (for more information, see Carbon Core Deprecations). |
| Provides dictionary lookup capabilities. |
| Provides a mechanism to notify clients about directories to re-scan to keep internal data structures up-to-date with the true state of the file system. |
| Contains interfaces for launching apps. |
| Contains interfaces for managing Spotlight metadata. |
| Contains interfaces for Open Transport and many hardware-related legacy Carbon managers. |
| Contains interfaces for the Search Kit. |
Quartz Framework
.net Framework 4.6.2 For Mac
Table A-7 lists the subframeworks of the Quartz framework (Quartz.framework).
Dot Net Download Page
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for finding, browsing, and displaying images. |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for displaying and managing PDF content. |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for playing Quartz Composer compositions in an app. |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for managing and applying filter effects to a graphics context. |
| Contains Objective-C interfaces for creating and managing a Quick Look preview panel, which is a UI object that displays preview items. |
WebKit Framework
Table A-8 lists the subframeworks of the WebKit framework (WebKit.framework).
Subframework | Description |
|---|---|
| Contains the library and resources for rendering HTML content in an HTMLView control. |
Xcode Frameworks
Xcode and all of its supporting tools and libraries reside in a portable directory structure. This directory structure makes it possible to have multiple versions of Xcode installed on a single system or to have Xcode installed on a portable hard drive that you plug in to your computer when you need to do development. This portability means that the frameworks required by the developer tools are installed in the /Library/Frameworks directory, where is the path to the Xcode installation directory. Table A-9 lists the frameworks that are located in this directory.
Framework | First available | Prefixes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xcode 5 |
| Interfaces for implementing unit tests in Objective-C. |
System Libraries
Some specialty libraries at the BSD level are not packaged as frameworks. Instead, OS X includes many dynamic libraries in the /usr/lib directory and its subdirectories. Dynamic shared libraries are identified by their .dylib extension. Header files for the libraries are located in the /usr/include directory.
OS X uses symbolic links to point to the most current version of most libraries. When linking to a dynamic shared library, use the symbolic link instead of a link to a specific version of the library. Library versions may change in future versions of OS X. If your software is linked to a specific version, that version might not always be available on the user's system.
Dotnet Hosting Download
Copyright © 2004, 2015 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Updated: 2015-09-16
